Business intelligence (abbreviated BI) is a set of analytical tools in the form of business information that is used to consolidate, analyze, store and access a lot of data in the context of business processes that lead to making decisions and actions with the aim of improving business or business performance.
Business intelligence provides an avenue for acquiring the knowledge needed to make good decisions. The business intelligence environment includes all the development, information processing, and support activities needed to provide reliable and highly relevant business information and business analytical capabilities for an organization’s business activities and for decision making.
Business intelligence explains a concept and method of how to improve the quality of business decision making based on data-based systems. Collections of raw data can be turned into information by analyzing and compiling based on the relationship between data by knowing what data to collect and in what context it is desired.
The function of business intelligence is as a decision support system where these systems and applications transform data within the organization (operational data, transactional data, or other data) into the form of knowledge with the general objective of presenting various information tailored to the needs of each user.
The following are definitions and definitions of business intelligence from several book sources:
- According to Laudon and Jane (2007), business intelligence is an analytical tool used to consolidate data, analyze, store and access large amounts of data to assist in decision making, such as software for database queries and reporting tools for multidimensional data analysis, and data mining.
- According to Vercellis (2009), business intelligence is a set of mathematical models and analytical methodologies that exploit available data to generate useful information and knowledge for complex decision-making processes.
- According to Yulianton (2008), business intelligence is all the exploration of business capital to benefit from the available data, either spread over different systems, or integrated in a centralized repository.
- According to Williams and Williams (2007), business intelligence is a set of business information and business analysis in the context of key business processes that lead to decisions and actions with the aim of enhancing information assets in key business processes to achieve improved business performance.
Benefits of Business Intelligence
According to Turban, Rainer and Potter (2011), the benefits and advantages obtained by using business intelligence in an organization or company include the following:
- Increase the value of organizational data and information . By building business intelligence, all data and information can be integrated so as to produce a conclusion from business conditions that is easy to access and understand so that it can help managers make better decisions.
- Facilitate measurement of organizational performance . In measuring the performance of an organization, a measure called the Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is often used. Business intelligence can easily show the achievement of an organization’s KPIs easily, quickly and precisely. Thus it will make it easier for the parties involved in decision-making to prepare anticipatory steps if there are indicators that indicate a problem or a target has not been achieved.
- Increase the value of existing information technology investments . Business intelligence does not always change or replace existing information systems, but only adds services to these systems so that data and information can be better represented.
- Improve cost efficiency . Business intelligence can increase cost efficiency because it can speed up someone in doing work thereby saving time and making it easier to use. The time needed to search for data and get the information needed is getting shorter and the way to get it doesn’t require special knowledge.
Types of Business
According to Turban (2007), there are five types of business intelligence, namely:
- Enterprise Reporting , used to generate static reports that are distributed to many people. This type of report is perfect for operational reports and dashboards.
- Cube Analysis , used to provide multidimensional OLTP analysis intended for business managers in constrained environments.
- Ad Hoc Query and Analysis , is used to provide access to users so they can perform queries on the database, and dig up information to the most basic level of transactional information. This query serves to explore the information carried out by the user.
- Statistical Analysis and Data Mining , used to perform predictive analysis or determine causal correlations between two matrices.
- Delivery Report and Alert , used proactively to send complete reports or provide warnings to large or large populations of users.
Business Intelligence Architecture
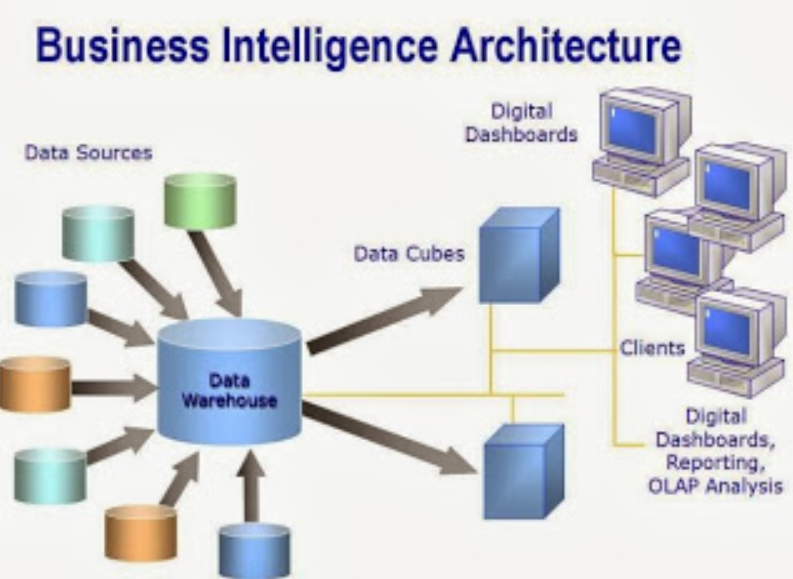
According to Rekha (2015), the business intelligence architecture is described below. The explanation of each component and stages in the business intelligence architecture is as follows:
a. Data Sources (Sumber Data)
This section functions to collect data and integrate data stored from various primary and secondary sources, this data is data owned by operational systems but can also include unstructured documents such as e-mail and data received from external providers, therefore in outline much is needed to unify and integrate data from disparate sources.
b. Data Movement dan Streaming Engines
Data movement and Streaming Engines are data that displays data from every integrated data variation which is obtained from various sources. Data Movement and Streaming Engines tasks are handled by a tool in the form of Extract Transform Load (ETL) which helps in finding data quality problems and facilitates the loading of large amounts of data into the warehouse.
The quality of the data is very important in assessing BI, if the data presented to the user is incomplete or inconsistent, it will not only fail, but will affect and hinder the decision-making process.
Meanwhile, The Complex Event Processing (CEP) is a tool that at the architectural level functions the same as the ETL tool, but ETL is used to process batch data and timeliness and is not critical, while CEP is used to handle real time or close to real time data. In some cases, CEP is useful for visualizing real time data access to support fast decisions.
c. Data Warehouse Servers
Data warehousing is subject-oriented, integrated, time-variable, and non-volatile collection of data to support decision-making processes. After the data is extracted, integrated and checked for data quality,
it is then loaded into a central repository or what is called a warehouse which is managed by one or more servers. The data warehouse is designed to recognize every topic of major concern related to business so that decision makers can analyze it easily.
d. Mid-tier servers
Mid-tier servers provide specialized functionality for different BI scenarios and include OLAP servers, Enterprise Search Engines, Data Mining Engines and Reporting Servers. An efficient OLAP server delivers multidimensional models to front end applications or directly to users. Users can perform sorting and selecting, aggregating, filtering, deriving and rotating data.
e. Front-end Application
Front-end applications are applications that are used directly by business users in making decisions. Examples of tools in the front-end application component are enterprise portals for searching, spread sheets and performance management applications that visualize such as dashboards or tools that allow users of these technologies to access by executing adhoc queries and tools that visualize data models. The more flexible these tools are the more they allow for more dynamic exploration of data and investigating data in different ways.
Use of Business Intelligenc
According to Darmawikarta (2003), business intelligence increases the value of organizational data and information. The existence of business intelligence facilitates monitoring of organizational performance, increases the value of existing investments, creates employees who have access to good information (well-informed workers) and increases cost efficiency. Following are some applications of using business intelligence to drive business value:
- Measurement , a program that creates a hierarchy of performance and benchmarking metrics that inform business leaders about progress towards business goals.
- Analytics , a program that builds quantitative processes for a business to arrive at optimal decisions and to conduct Business Knowledge Discovery. Often includes data mining, statistical analysis, predictive analysis, predictive modeling, business process modeling.
- Reporting/Enterprise Reporting , a program that builds a Strategic Reporting infrastructure to serve business strategic management, not Operational Reporting. Often involves Data visualization, Information systems executive, OLAP.
- Collaboration/Collaboration platforms , programs that get different areas (both inside and outside the business) to work together through data sharing and Electronic Data Interchange.
- Knowledge Management , a program to make enterprise data driven through strategies and practices to identify, create, display, distribute, and enable the adoption of insights and experiences that are true to business knowledge. Knowledge Management Compliance leads to Learning Management and Regulatory Compliance.
Bibliography
- Laudon, KC, and Jane, PL 2007. Management Information System . Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
- Vercellis, Bernadth. 2009. Information Systems . Yogyakarta: Lokomedia.
Also Read :
- 8 Amazing Examples Of Corporate Fitness Programs Fostering Employee Health
- Best Technology Institute Utilizing Web Hosting
- 5 Differences between Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3 Competitive Intelligence Factors So that Businesses Are Superior to Competitors
- The 8 Most Used Business Intelligence Tools 2023